Transduction Protocol for RAW 264.7 Cells: A Complete, Ready-to-use Workflow
Nov 25,2025
RAW 264.7 cells, a widely used murine macrophage line, serve as a standard model for investigating innate immune pathways, inflammatory responses, and drug delivery mechanisms in immunological research. However, their pronounced phagocytic activity, combined with the cytotoxicity of many conventional transfection reagents, has historically limited transfection efficiency. Advances in mRNA transfection methodologies are increasingly overcoming these constraints.
In this issue of Cell Culture Academy, we summarize the key biological characteristics of RAW 264.7 cells and describe practical, experimentally validated approaches for achieving high-efficiency mRNA transfection.
Ⅰ. Introduction to RAW 264.7 Cells
The RAW 264.7 cells, originally derived from an Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced tumor in male BALB/c mice, is a macrophage-like lineage exhibiting well-defined functional characteristics. Key features include:
● Predominantly rounded morphology with a minor population of spindle-shaped cells.
● Expression of integrin receptors CD49d and CD11b, facilitating interactions with VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 on inflamed vascular endothelium, with high phagocytic activity.
● Secrete a wide array of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
● Demonstrate neutral red uptake, efficiently phagocytize latex beads and zymosan particles, and mediate antibody-dependent lysis of sheep erythrocytes and tumor target cells.
Characterized by adherent growth, rapid proliferation, and extensive functional profiling, RAW 264.7, often dubbed the "macrophage sprites" of the mouse peritoneum, have become evergreen performers on the stage of inflammation and immunology research.
They respond robustly to stimuli such as lipopolysaccharides and zymosan through coordinated activation of TLR-NF-κB signaling, NLRP3 inflammasome assembly, and osteoclast differentiation. This functional versatility enables a broad range of experimental applications, including studies of pathogen–host interactions, evaluation of nanotherapeutics, and in vitro screening of nucleic acid-based vaccines.
Ⅱ. Challenges in Culturing the RAW 264.7 Cells
The RAW 264.7 cell line is inherently delicate, and its cultivation is often complicated by several factors:
● High sensitivity to serum quality: FBS with elevated endotoxin or lipoprotein levels can trigger rapid differentiation, resulting in the formation of rigid polygonal protrusions. These differentiated cells exhibit strong adhesion but reduced transfection efficiency.
● Limited intrinsic adherence: Routine washing with PBS during medium changes can readily detach cells.
● Unsuitability for trypsin digestion: Exposure to trypsin activates cellular signaling pathways, increasing experimental background and complicating downstream analyses.
Recommended Subculturing Practices for RAW 264.7 Cells:
● Culturing in RAW 264.7 Cell Complete Medium.
● Subculturing at 70-80% confluency by gently pipetting to detach cells; cell scrapers may be used if necessary.
● Adding pre-warmed (37℃) medium during medium changes to minimize cold-induced stress.
● Cryopreserving low-passage cells (P3-P5) as “young” seed stocks in liquid nitrogen, with routine mycoplasma screening to preserve transfection competence and undifferentiated status.
Ⅲ. mRNA Transfection Strategy
The nuclear envelope and lysosomal degradation pathways intrinsic to RAW 264.7 cells present substantial obstacles to efficient plasmid DNA expression. Introduction of exogenous DNA can trigger Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) signaling, leading to cytokine secretion and nitric oxideproduction, which may compromise cellular integrity and reduce experimental reproducibility.
Recent developments in chemically modified nucleotides and high-efficiency liposomal carriers have positioned mRNA delivery as a robust solution to these challenges. Pricella® introduces Mergene1000® RAW 264.7 Cell-Specific mRNA Transfection Reagent, offering the following advantages:
● Direct cytosolic delivery: mRNA is delivered straight to the cytoplasm, bypassing nuclear entry and transcriptional barriers.
● Cell-specific optimization: Specifically designed for RAW 264.7 cells, achieving enhanced transfection efficiency.
● Improved stability: Exhibits low cytotoxicity and superior reagent stability.
● Streamlined workflow: User-friendly protocol ensures consistent and reproducible results.
Product Operation Flowchart
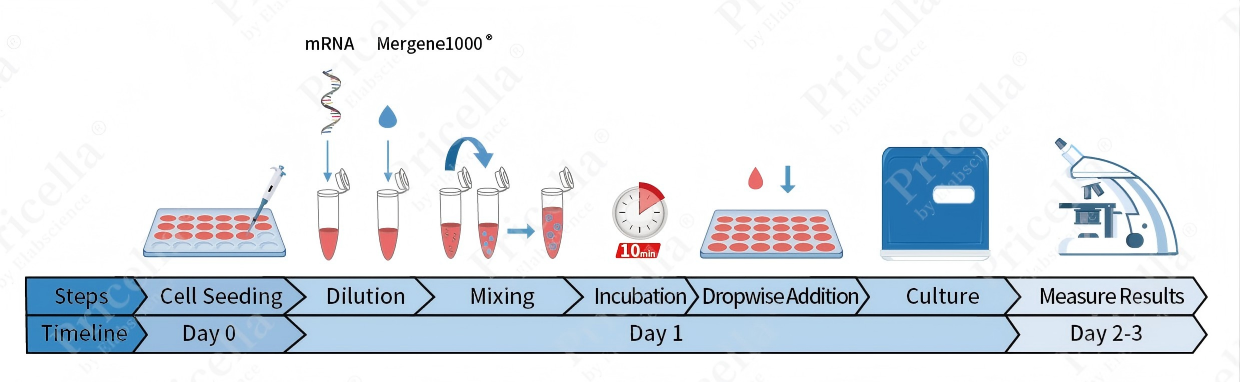
Figure 1. Product operation flowchart
Usage Steps
1.Cell Preparation
Seed RAW 264.7 cells at a density of 1.2×105 cells per well in 500 μL of RAW 264.7 Cell Complete Medium, one day prior to transfection. Incubate for approximately 12 h. Adjust the incubation period according to observed cell morphology to achieve 70-90% confluency at the time of transfection.
2.Cell Transfection
Prepare a sterile centrifuge tube. Add 50 μL of high-glucose DMEM, followed by 0. 6 μL of Mergene1000® RAW 264.7 Cell Specific mRNA Transfection Reagent. Mix gently by pipetting.
Add 0.2 μg of mRNA to the diluted transfection complex and mix by gentle pipetting. Incubate the mixture at ambient temperature (20-25℃) for 5-10 min.
Add the mixture dropwise to the cultured cells. Gently homogenize the culture plate using a figure-eight swirling motion.
Transfer the plate to a humidified incubator maintained at 37℃ with 5% CO2, performed 12-24 h post-transfection.
3.Transfection Performance
The enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene was delivered into RAW 264.7 cells using both the Mergene1000® RAW 264.7 Cell-Specific DNA Transfection Reagent and T Brand L3000. Quantitative evaluation was conducted via fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry (FCM) (Figure 2).
Figure 2. RAW 264.7 cells transfected with EGFP expression plasmid
(The comparison experiment was strictly conducted according to the instructions in the product manuals.)
Ⅳ. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1.Why is transfection efficiency low in RAW 264.7 cells?
As professional phagocytes, RAW 264.7 cells possess intrinsic defense mechanisms against exogenous DNA. Introduction of foreign nucleic acids can activate the TLR9 signaling pathway, triggering cytokine secretion and nitric oxide production, which may compromise cell viability.
2.Is serum-free medium required for transfecting RAW 264.7 cells?
No. When using Mergene1000® RAW 264.7 Cell-Specific mRNA Transfection Reagent, neither removal of transfection complexes nor post-transfection medium replacement is necessary. Optionally, medium may be replaced 4–6 h post-transfection depending on cell condition.
3.How can transfection efficiency be enhanced?
Using high-purity mRNA;
Maintaining cell confluency between 70% and 90% at the time of transfection.
4.How does weak cell adhesion affect transfection?
RAW 264.7 cells inherently exhibit poor adhesion. Rough handling during transfection can dislodge cells and reduce efficiency. To minimize stress, avoid vigorous pipetting or agitation, and consider shortening the incubation time of the transfection complex.
5.How should severe post-transfection cell death be addressed?
Use log-phase cells with optimal viability, avoiding over-passaged or contaminated cultures;
Adjust nucleic acid or transfection reagent quantities appropriately;
Optionally replace medium 4-6 h post-transfection based on cell condition.
6.How can excessive post-transfection differentiation be managed?
Employing RAW 264.7 cell-specific medium optimized for maintaining phenotype;
Gentle handling during passaging, removing firmly adhered differentiated cells;
Shortening transfection duration if necessary.
RAW 264.7 macrophages remain a central model in innate immunity research, spanning applications from pathogen infection studies and nanovaccine development to investigations of signaling pathwaysand gene editing. By understanding their functional characteristics and applying optimized mRNA transfection protocols, these murine peritoneal-derived cells continue to serve as key regulators of inflammatory and defense responses within in vitro culture systems.
Prev: Alzheimer's Disease Research: Pricella® Cell Lines: Your Trusted Partner for In Vitro Models
Next: Analysis of Cell Culture Medium: Composition, Preparation, and Troubleshooting

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

